| Description |
Labelled |
Unlabelled |
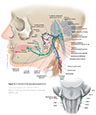
Figure IX–1 Overview of the glossopharyngeal nerve.
General sensory afferent (blue-green)
Visceral sensory afferent (purple)
Special sensory afferent (green)
Somatic motor efferent (pink)
Branchial motor efferent (yellow)
Visceral motor (parasympathetic) efferent (blue) |
 |
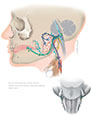 |
Figure IX–2 Tympanic branch of cranial nerve IX (cut through the petrous temporal bone).
General sensory afferent (blue-green)
Visceral sensory afferent (purple)
Special sensory afferent (green)
Somatic motor efferent (pink)
Branchial motor efferent (yellow)
Visceral motor (parasympathetic) efferent (blue) |
 |
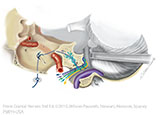 |
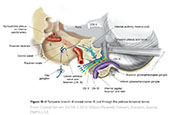
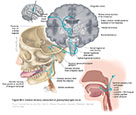
Figure IX-3 General sensory component of glossopharyngeal nerve.
General sensory afferent (blue-green) |
 |
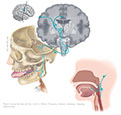 |
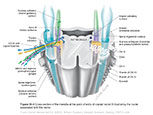
Figure IX-4 Cross-section of the medulla at the point of entry of cranial nerve IX illustrating the nuclei associated with this nerve.
General sensory afferent (blue-green)
Visceral sensory afferent (purple)
Special sensory afferent (green)
Somatic motor efferent (pink)
Branchial motor efferent (yellow)
Visceral motor (parasympathetic) efferent (blue) |
 |
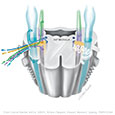 |
Figure IX-5 The bifurcation of the common carotid artery demonstrating CN IX sensory signals from baroreceptors in the wall of the carotid sinus and chemoreceptors within the carotid body as well as parasympathetic efferents that are vasodilatory to vessels of the carotid body and sinus. (The carotid body is enlarged to show structural detail.
Visceral sensory afferent (purple)
Visceral motor (parasympathetic) efferent (blue) |
 |
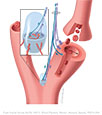 |
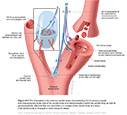
Figure IX–6 Visceral sensory component of the glossopharyngeal nerve—elevated brain stem.
Visceral sensory afferent (purple) |
 |
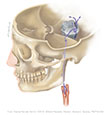 |
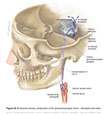
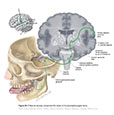
Figure IX–7 Special sensory component (for taste) of the glossopharyngeal nerve.
Special sensory afferent (green) |
 |
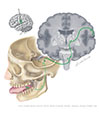 |
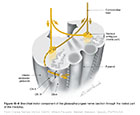
Figure IX–8 Branchial motor component of the glossopharyngeal nerve (section through the rostral part of the medulla).
Branchial motor efferent (yellow) |
 |
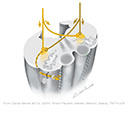 |
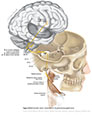
Figure IX–9 Branchial motor component of the glossopharyngeal nerve.
Branchial motor efferent (yellow) |
 |
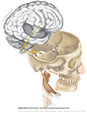 |
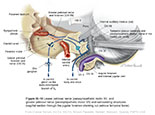
Figure IX–10 Lesser petrosal nerve (parasympathetic motor IX) and greater petrosal nerve (parasympathetic motor VII) and surrounding structures(sagittal section through the jugular foramen showing cut petrous temporal bone).
Visceral motor (parasympathetic) efferent (blue) |
 |
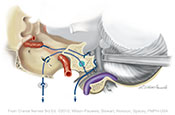 |
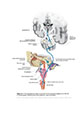
Figure IX–11 Parasympathetic motor components of the glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX) to: parotid gland, internal carotid artery and sinus, and carotid body.
Visceral motor (parasympathetic) efferent (blue) |
 |
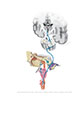 |
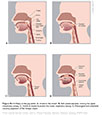
| Figure IX–12 Steps in the gag reflex. A, Irritant in the mouth. B, Soft palate elevates, closing the upper respiratory airway. C, Glottis is closed to protect the lower respiratory airway. D, Pharyngeal wall constricts causing expulsion of the foreign object. |
 |
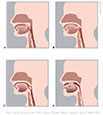 |
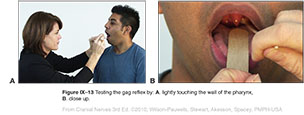
| Figure IX–13 Testing the gag reflex by: A. lightly touching the wall of the pharynx, B. close up. |
 |
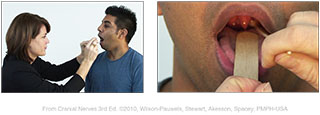 |
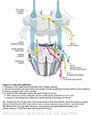
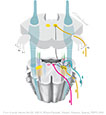
Figure IX-14 Gag reflex pathways.
General sensory afferent (blue-green)
Somatic motor efferent (pink)
Branchial motor efferent (yellow) |
 |
 |