| Description |
Labelled |
Unlabelled |
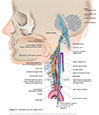
Figure X–1 Overview of the left vagus nerve.
General sensory afferent (blue-green)
Visceral sensory afferent (purple)
Branchial motor efferent (yellow)
Visceral motor (parasympathetic) efferent (blue |
 |
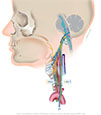 |
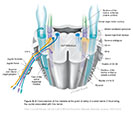
Figure X–2 Cross-section of the medulla at the point of entry of cranial nerve X illustrating the nuclei associated with this nerve.
General sensory afferent (blue-green)
Visceral sensory afferent (purple)
Special sensory afferent (green)
Branchial motor efferent (yellow)
Visceral motor (parasympathetic) efferent (blue) |
 |
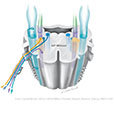 |
Figure X–3 Cross-section through the rostral (open) medulla demonstrating the branchial motor component of cranial nerve X including spinal rootlets of cranial nerve XI.
Branchial motor efferent (yellow) |
 |
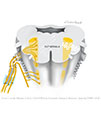 |
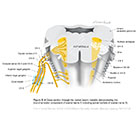
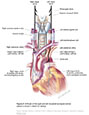
| Figure X–4 Route of the right and left recurrent laryngeal nerves (nerve is shown in black for clarity). |
 |
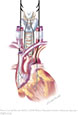 |
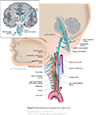
Figure X–5 General sensory component of the vagus nerve.
General sensory afferent (blue-green) |
 |
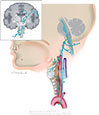 |
Figure X–6 Schematic illustration depicting visceral and general sensory components of the left vagus nerve from the larynx.
General sensory afferent (blue-green)
Visceral sensory afferent (purple) |
 |
 |
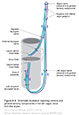
Figure IX–7 Special sensory component (for taste) of the glossopharyngeal nerve.
Visceral sensory afferent (purple)) |
 |
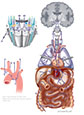 |
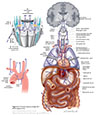
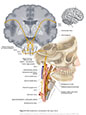
Figure X–8 Branchial motor component of the vagus nerve.
Branchial motor efferent (yellow) |
 |
 |
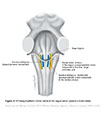
| Figure X–9 Parasympathetic motor nuclei of the vagus nerve (posterior brain stem). |
 |
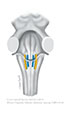 |
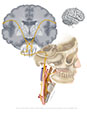
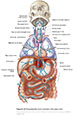
Figure X–10 Parasympathetic motor component of the vagus nerve.
Visceral motor (parasympathetic) efferent (blue) |
 |
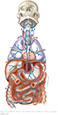 |
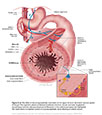
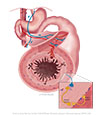
Figure X–11 The effect of the parasympathetic innervation of the vagus nerve on the enteric nervous system of the gut. The myenteric plexus (of Auerbach) between the inner circular and outer longitudinal muscle layers and the submucosal plexus (of Meissner) in the submucosal space are highlighted. The insert shows a simplified version of a parasympathetic nerve affecting an enteric neuron.
Visceral motor (parasympathetic) efferent (blue) |
 |
 |
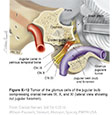
| Figure X–12 Tumor of the glomus cells of the jugular bulb compressing cranial nerves IX, X, and XI (lateral view showing cut jugular foramen).. |
 |
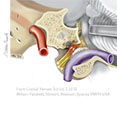 |
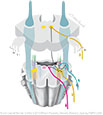
Figure X-13 Gag reflex pathways.
General sensory afferent (blue-green)
Somatic motor efferent (pink)
Branchial motor efferent (yellow) |
 |
 |
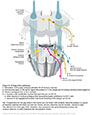
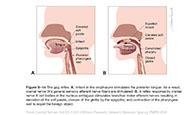
| Figure X–14 The gag reflex. A, Irritant in the oropharynx stimulates the posterior tongue. As a result, cranial nerve IX's general sensory afferent nerve fibers are stimulated. B, A reflex response by cranial nerve X cell bodies in the nucleus ambiguus stimulates branchial motor efferent nerves resulting in elevation of the soft palate, closure of the glottis by the epiglottis, and contraction of the pharyngeal wall to expel the foreign object |
 |
 |
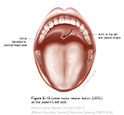
| Figure X–15 Lower motor neuron lesion (LMNL) on the patient’s left side. |
 |
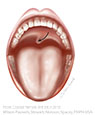 |